How to choose thermal grease
The performance of the cooling system depends on the quality of the thermal paste. A layer made of inappropriate material can lead to processor overheating even with a powerful cooler.
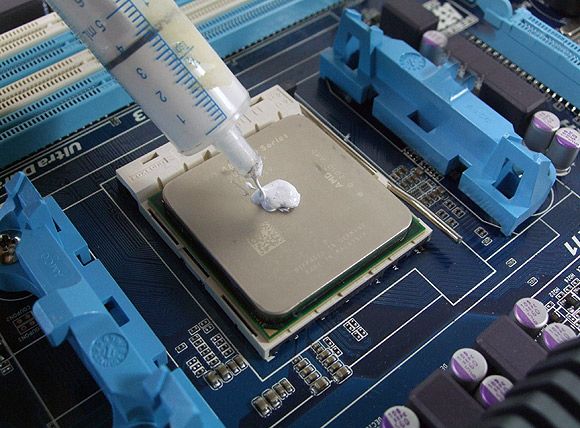
How to choose thermal grease for the processor and for the video card: what characteristics to pay attention
When choosing a thermal paste for a laptop, system unit and its components, you should pay attention to the following technical characteristics of this material:
-
Thermal conductivity and thermal resistance (measured values);
-
Plasticity, resistance to temperature changes (unmeasured values);
In addition, it is important to determine whether it is necessary thermal paste or more appropriate to apply thermal jets.
Thermal characteristics
The most serious influence on the performance of thermal paste has its thermal characteristics. They have two of this material - thermal conductivity and thermal resistance.
Thermal capacity of thermal paste is a parameter that shows the intensity with which this material removes heat from a processor or a computing chip. It is measured in W / (m × K). The higher the heat capacity - the better the thermal paste transfers heat from the processor to the radiator contact pad.
-
Thermal grease with a thermal conductivity of 3-5 W / (m × K) is suitable for desktop computers and server systems. Moreover, the higher the processor performance - the greater should be the value of this parameter. It is worth considering that the “old” chips often heat up much more strongly than the more modern ones, and therefore they need better thermal grease.
-
For laptops that are equipped with a cooling system with low productivity, thermal grease with a high value of heat capacity - 6-10 W / (m × K) will be required. This will minimize the risks of throttling and processor overheating, even if the computer is on its knees and therefore its lower air intake vents are closed.
Thermal resistance is a parameter, from the operational point of view, the inverse of heat-moisture. The smaller its value, the better the thermal grease "copes with its responsibilities." However, it does not play a critical role in the choice of material; therefore, it is recommended to evaluate precisely the heat capacity.
Ductility and resistance to temperature changes
Plasticity and resistance to temperature changes - values that are not normally measured. However, they are also important. You can only estimate the values of these parameters indirectly.
It depends on the resistance to temperature changes how quickly the thermal paste dries and after what time it will be necessary to change it. This parameter can be indirectly determined from the operating temperature range of this material. The wider it is - the higher the stability. For example, thermal grease Zalman ZM-STG2 has a working temperature range from -40 to +150 degrees Celsius. This ensures that it will not dry for a long time.
Ease of application of thermal paste depends on plasticity. Indirectly, this parameter can be determined on the basis of the operating temperature range and heat capacity. Than they are correspondingly wider and larger - the thicker the thermal paste will be and therefore difficult to apply.
Composition

The composition of thermal paste directly determines its heat content. In addition to polydimethylsiloxane fluid, it includes various metals. And it is their thermal conductivity that determines the thermal moisture of thermal paste.
-
Low cost thermal paste varieties, such as KTP-8, are usually made of zinc. This metal has good, but not perfect heat and water. Such thermal paste is suitable for use except in older computers with low-power processors and low TDP values.
-
Premium types of thermal paste are made of metals with high thermal conductivity, such as tungsten, copper, silver and gold. Often, these materials are even painted in the characteristic colors of these substances.
Such thermal paste is well suited for powerful computing chips - processors with a TDP of more than 60 W, as well as video card cores.
Thermal paste or thermopad

In some cooling systems, laptops do not use thermal grease, but thermocouples - special heat-conducting cushions between the processor or video card's computing chip and the heatsink base.
Thermocouples are used in the case when the physical size of the chip is too small for contact with the base of the radiator through the thermal paste layer. They have low thermal conductivity, so they are mainly used for cooling low-powered computer components (processors and video cards with low performance).
When choosing a thermopad it is also worth considering its heat and thermal resistance.
But it is worth considering that if the design of the radiator or chip allows the use of thermal grease, and not thermal dip, then it is worth using thermal paste.
Manufacturers
Among the manufacturers of thermal paste can be identified:
-
Companies producing KTP-8 and Alsil-3. KTP-8 is the most affordable and widely used thermal grease. However, due to the low thermal capacity (less than W / (m × K)), it is suitable only for very old computers. Alsil-3 is another version of the budget thermal paste. Its thermal capacity is 1.8 W / (m × K), so it is also suitable only for very old computers;
-
Deepcool, Evercool - produce both low cost and premium thermal paste. Suitable for low-power home and office computers, as they may have a low temperature range;
-
Zalman, Titan, Arctic Cooling, Thermal Grizzly - produce high-quality thermal grease that has good values of heat, high temperature range of work and low thermal resistance. The only drawback is the relatively high price.
By the way, the company Thermal Grizzly also produces high-quality thermocouples with copper or gold, which are used as heat conductors.
In the next article, our experts tell how to choose a disc for recording.
Attention! This material is the subjective opinion of the authors of the project and is not a guide to purchase.













